Did you know that 80% of Americans eat fast food? It’s not just millennials, Hispanics, and Blacks. According to a recent study, this number has increased even more over the past few years, with the average American consuming about two-thirds of this type of food daily.
80% of Americans eat fast food
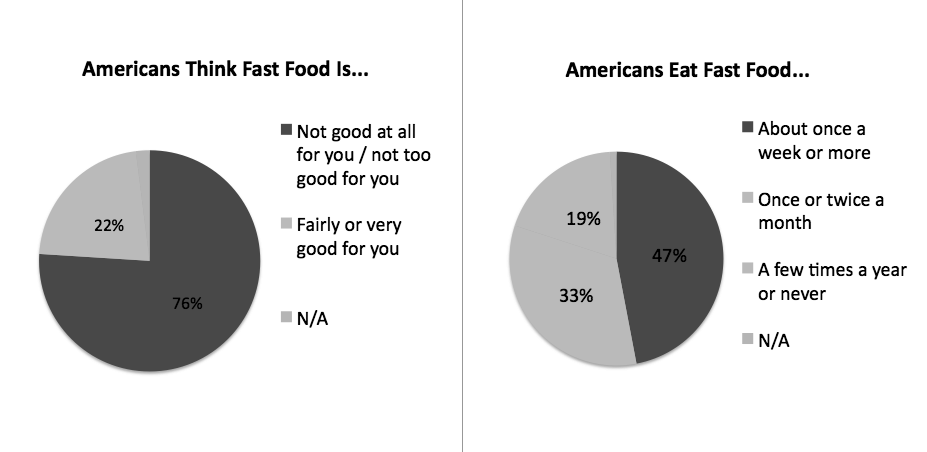
Fast food has become an American staple and is now a significant source of calories and fat. In 2003, 76 percent of American adults reported eating fast food at least once weekly. This consumption peaks among young adults, with 57% of those under 30 reporting eating fast food at least once a week. As people age, however, their fast-food intake decreases, with the percentage dropping to 47% for those aged 30 to 49 and 40% for those over 65.
The American Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recently released a data brief on the health risks associated with fast food. The report found that fast-food consumption is not only high in calories but is also associated with a higher risk of disease. Despite the health risks of fast-food consumption, many adults still eat it despite its many health risks.
According to the report, the percentage of adults who consume fast food varies by income, age, race, and sex. The highest proportion of adults aged 20 to 39 reported eating fast food in the past day, followed by adults aged 40 to 59. Only 24 percent of people over sixty said eating fast food for breakfast or a snack. Fast-food consumption accounts for 11.3% of the average American diet.
Many Americans eat fast food because it is inexpensive and convenient. Fast food is more affordable for those with higher incomes than those with lower incomes. A third of Americans earning less than $20,000 per year eat fast food on an average week.
Millennials
Fast-food restaurants have struggled to keep up with the millennial consumer, who tends to eat more health-conscious and less processed items. While the comfort-food feeling is still a vital component of the fast food industry, newer generations choose to eat more sustainably and ethically and consume organic and local food. Despite these trends, some articles argue that millennials are causing the fast food industry to fail.

The Millennial generation is a highly influential demographic, with many actively engaging in social media and using the Internet for research. This means that Millennials are a potential market for advertisers and marketers. In addition to being influential, they share many attitudes and values. For example, they consider healthy eating a positive social activity. However, they admit that they don’t always eat healthily and tend to eat fast food instead of healthier options.
Grocery stores have changed dramatically in the past century. In the early 1900s, the shelves were dominated by big brands. Later, freezers led to a booming frozen food business. Today’s millennials are more health conscious, and grocery stores are working to appeal to them.
The study also looked at whether fast foods were popular with millennials. The Millennials were more likely to buy fast food than non-millennials. As a result, they were likely to gain weight. In addition to the high-fat content of fast food, they were also likely to increase their body mass index (BMI) – a measurement of body fat. A BMI of 25 kg/m2 is considered overweight, and above 30 kg/m2 is considered obese.
Blacks
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention studied how adult Americans consume fast food. One in every three adults eats fast food at least once a week. This number is higher among young adults, blacks, and Hispanics and lower among older whites.
The findings were based on a survey that included 8,000 adults. This survey revealed that those who eat fast food are likelier to spend less time on leisure and work than those who do not consume fast food. This study also shows that people from the South and the Midwest have significantly higher concentrations of fast food joints than those in other parts of the country. Alabama has more than six times the number of fast food outlets than Vermont.
The CDC study also reveals that the rate of fast food consumption in adults increased along with income. While the percentage of adults who eat fast food increased as income increased, people who earn under the poverty line ate fast food more often than those who made over 350 percent of the poverty line, or $112,950 per year for a family of four. Furthermore, fast food is more prevalent in lower-income neighborhoods, while people in more expensive areas eat less.

There is no denying that fast food has become ubiquitous in American society. From humble hot dog stands in Southern California to stadiums, airports, and train stations, fast food has permeated nearly every nook of American life. It is served in almost every restaurant, drive-through, and hospital cafeteria.
Hispanics
Fast food is a popular means for Latinos to meet their nutritional needs, and fast food chains have spread across the country. Every year, new brands enter the market. According to Zambrana and Carter-Pokras (2010), fast foods are more affordable than other nutrition methods and can be easily prepared at home.
Studies have shown that Hispanics eat more fattening foods than Americans. This is because they are generally less aware of the higher fat content in foods. They also consume more meat than other groups. This means that Hispanics tend to eat more saturated fats.
The rapid urbanization of the United States has affected the health of the Hispanic population. Many Hispanics were originally from rural Mexico, so the rapid urbanization has made it difficult for them to practice alternative nutrition. In addition to being unable to eat alternative foods, these individuals cannot afford healthy foods.
In the late 20th century, the number of Latinos living in the United States reached unprecedented levels. Most of these immigrants came from northern and central Mexico and Puerto Rico. However, Latinos from other parts of Latin America also began to migrate to the U.S., partly because of the Immigration Reform Act of 1965, which set strict quotas for immigrants born in the Americas. Likewise, due to the Cold War’s involvement in the region, displaced populations from Central and South America also arrived in the U.S.
Fast food chains are trying to appeal to Hispanics by promoting their products in ads and promotions. Almost 40% of advertisements for fast food for children on Spanish-language television in 2019 targeted Hispanics, up from 33% in 2012. McDonald’s was the most popular brand among Hispanic families, and its Happy Meals promotion attracted Hispanic parents.
Those with less leisure time
The prevalence of fast food consumption is higher among those who live in the South and central cities. This group is also more likely to own a car and live in areas with dense populations. This study used generalized linear models and adjusted for potential confounding variables to determine why people eat fast food more often.
The study also examined whether people’s fast food consumption was related to income. People in the lowest income bracket ate 3.6 fast-food meals per week, while those in the middle-income bracket ate 4.2. In the highest income bracket, the association was not as strong. The researchers also found that smokers and the middle class tended to be less health-conscious. In addition, obesity was less likely among those who used nutritional labels.
Those with less income
One recent study showed that people from all income levels eat about the same amount of fast food. The lowest income group reported eating at least 3.6 fast-food meals a week, while people from middle and high-income groups ate three or more meals. In total, 79% of respondents reported eating fast food at least once a week, while 23% bought at least three meals. The study also examined the relationship between fast food consumption and participants’ wealth levels. While the results were similar, Zagorsky said that the study’s results should not be taken for granted.
People with higher fast-food exposure levels also had higher body fat levels than those with lower fast-food consumption. These individuals reported having lower levels of income and fewer educational qualifications. Further, people with the highest fast-food exposure levels had higher BMIs and processed meat intake and were more likely to be obese.
Higher-income individuals spend more money on eating out. This is partly why the restaurant industry has focused on offering the rich a variety of reasons to dine out, including Shake Shack, Sweetgreen, and Panera Bread. However, the average American household spends about 10% of its income on fast food. Fast food is a cheap and convenient way to indulge without spending much time or money cooking.
The CDC study also found that the prevalence of fast-food consumption increased as income increased. Those earning less than $110,000 a year were most likely to eat fast food daily, while people earning more than $75,000 a year were less likely to do so.

